Street cameras record footage for security, traffic monitoring, and law enforcement, but also raise privacy concerns, requiring careful management and oversight.
Types of Street Cameras and Their Recording Features:
Street cameras come in various types, each with distinct recording capabilities. Fixed cameras are mounted in a stationary position, offering continuous recording of a specific area.
Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) cameras allow for dynamic coverage, with the ability to move and zoom in on areas of interest, often recording only when there is significant activity. Bullet cameras, known for their long shape, are typically weatherproof and used for outdoor recording.
Dome cameras, often seen indoors, are designed for 360-degree coverage. The recording features vary by type, including resolution quality, recording modes, and storage options.
The Evolution of Street Cameras:
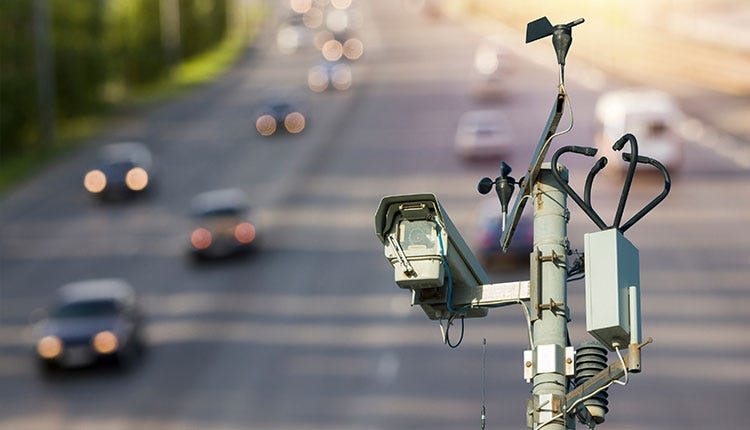

Street camera technology has undergone significant advancements, transitioning from analog to digital systems. Initially, analog cameras captured footage on tapes, limiting storage capacity and requiring manual management.
These systems offered basic recording but lacked advanced features. With the advent of digital technology, street cameras now record in high-definition, providing clearer and more detailed images.
IP cameras introduced networked recording, allowing footage to be stored on digital servers or cloud systems, with easier access and better security. This evolution has enhanced the efficiency, reliability, and accessibility of recorded surveillance footage.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Street Camera Recording:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing street camera recording, adding layers of sophistication and efficiency. AI enables smart surveillance, where cameras can identify specific activities or objects, such as recognizing faces, license plates, or detecting unusual behavior.
This technology enhances the usefulness of recorded footage by focusing on relevant events, reducing the need for constant human monitoring. AI also powers predictive analytics, allowing systems to anticipate and alert authorities to potential incidents before they occur.
The integration of AI in street cameras is making surveillance more proactive and effective in maintaining public safety.
Data Security and Management of Recorded Footage
The security and management of recorded footage are critical to ensuring privacy and data integrity. Footage is typically stored in encrypted formats to prevent unauthorized access, with strict access controls in place to limit who can view or retrieve the recordings.
Data management protocols ensure that footage is stored efficiently, often using cloud storage for scalability. Regular audits and monitoring help detect any security breaches, and data retention policies dictate how long footage is kept before it is automatically deleted.
These measures are essential in protecting sensitive information and maintaining public trust in surveillance systems.
Street Cameras in Urban vs. Rural Areas:
The deployment and recording practices of street cameras differ significantly between urban and rural areas. In urban areas, cameras are more densely installed due to higher population densities and increased security needs.
These cameras often have advanced features, including high-resolution recording and networked systems for real-time monitoring. In contrast, rural areas typically have fewer cameras, with a focus on specific locations such as main roads or community centers.
Recording practices may also vary, with rural systems often using simpler, more cost-effective technology. The contrast in camera use reflects the differing security priorities and challenges in these environments.
Ethical Implications of Street Camera Recordings:
The widespread use of street cameras raises important ethical questions about surveillance and privacy. While these cameras enhance public safety, they also monitor individuals’ activities in public spaces, sometimes without explicit consent.
This can lead to concerns about mass surveillance and the potential misuse of recorded data. Ethical considerations include the balance between security needs and the right to privacy, as well as the transparency of surveillance practices.
Ensuring that the use of street cameras adheres to ethical guidelines and legal standards is crucial in maintaining public trust and protecting civil liberties.
Also read: A Camera Operator is Filming a Nature Explorer – The Role of Camera!
The Cost and Maintenance of Street Camera Recording Systems:
The installation and upkeep of street camera recording systems involve considerable costs. Initial expenses include the purchase of cameras, recording equipment, and network infrastructure.
Additionally, there are ongoing costs related to maintenance, such as regular inspections, repairs, and software updates. The cost also extends to data storage, especially for high-definition footage, requiring significant investment in either physical or cloud-based storage solutions.
Municipalities and organizations must budget for these expenses to ensure continuous operation and reliability. However, the investment is often justified by the enhanced security and crime prevention benefits provided by these systems.
Public Perception and Acceptance of Street Camera Recordings:
Public perception of street camera recordings varies, with opinions influenced by factors such as location, privacy concerns, and perceived benefits. In areas with high crime rates, residents may view street cameras as necessary for safety, appreciating the deterrent effect on criminal activities.
Conversely, in locations where privacy is highly valued, there may be resistance to constant surveillance. Public acceptance is often higher when authorities are transparent about the purpose of the cameras and how the recorded footage is used.
Community engagement and education can help bridge the gap between security needs and privacy concerns, fostering greater public support.
Legal Challenges and Court Cases Involving Street Camera Footage:

Street camera footage has been central to numerous legal challenges and court cases, highlighting its impact on law enforcement and privacy rights. In criminal investigations, recorded footage often serves as crucial evidence, helping to identify suspects and reconstruct events.
However, there have been instances where the use of surveillance footage has raised legal concerns, particularly regarding privacy violations and the legality of recording in certain areas.
Courts have had to balance the evidentiary value of such footage against individuals’ rights to privacy. These cases underscore the need for clear legal frameworks governing the use of street camera recordings.
The Future of Street Camera Recording:
The future of street camera recording is set to be shaped by technological advancements and societal trends. Innovations such as higher resolution cameras, improved AI capabilities, and more secure storage solutions are likely to enhance the effectiveness of surveillance systems.
Additionally, the integration of smart city technologies will see street cameras becoming part of larger, interconnected networks, offering real-time data for public safety, traffic management, and urban planning.
However, as these systems become more advanced, there will also be increased scrutiny on their ethical use, requiring ongoing dialogue and regulatory updates to address emerging privacy concerns.
FAQ’s:
1. Do street cameras record continuously?
Yes, many street cameras record continuously, though some are motion-activated or use loop recording to save storage space.
2. How long is the footage from street cameras stored?
The storage duration varies, typically ranging from a few days to several months, depending on storage capacity and legal requirements.
3. Are street camera recordings secure?
Yes, recorded footage is usually stored securely with encryption and restricted access to protect against unauthorized use.
4. Can the public access street camera recordings?
Generally, public access to street camera footage is restricted and is typically available only through legal or official requests.
5. Do street cameras raise privacy concerns?
Yes, the use of street cameras can raise privacy issues, leading to ethical and legal debates on the balance between public safety and individual privacy rights.
Conclusion:
Street cameras play a vital role in enhancing public safety by recording footage used for crime prevention, traffic monitoring, and law enforcement. While their benefits are significant, they also raise important privacy concerns that must be carefully managed through clear regulations and ethical guidelines.
Related Post:








































Leave a Reply